Publication History
Submitted: April 27, 2024
Accepted: May 22, 2024
Published: February 28, 2025
Identification
D-0347
DOI
https://doi.org/10.71017/djnsi.4.2.d-0347
Citation
Kamal Giri (2025). First Principles Study of Stability of Sodium Hydride (Nah)N Clusters, (N=1-6). Dinkum Journal of Natural & Scientific Innovations, 4(02):92-103.
Copyright
© 2025 The Author(s).
92-103
First Principles Study of Stability of Sodium Hydride (Nah)N Clusters, (N=1-6)Original Article
Kamal Giri 1*
- Lecturer in Physics at Liverpool International College, Kathmandu, Nepal.
* Correspondence: lovdrazzk@gmail.com
Abstract: This entire work described the structures and electronic properties of sodium hydride clusters (Na H) n (n=1-6), where n is the number of atoms) by the first principles study. In the calculation, ab-initio, Density Functional Theory (DFT) and AIM (Atom in Molecule) theoretical calculation have been used. DFT and ab-initio were performed implementing Gaussian 03W suite of software. For AIM theoretical calculation AIMALL software was used. We have calculated all the physical properties such as interaction energy, corrected zero-point energy, and corrected interaction energy, ground state energy of sodium hydride clusters. The calculated corrected interaction energy of (Na H) n, (n=2-6) clusters, have been found to be in the range (-19.131 to – 22.289) kcal mol−1 for linear structures and the range (-22.620 to -35.779) kcal mol−1 for cyclic structures at DFT (B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. Sodium hydride cluster found to be more stable in the singlet state than the triplet state. The linear structure of sodium hydride cluster is found to have maximum frequency compared to other structures like cyclic and cubic. Also, we have analyzed different form of stretching and contracting frequencies of sodium hydride clusters. The electron density at bond critical point and Laplacian of (Na H) n (n=1-6) clusters, have been found to be in the range (0.0269 to 0.0327) a. u and (0.1036 to 0.1298) a. u for linear structures and the range (0.0220 to 0.0238) a. u and (0.0803 to 0.0938) a. u cyclic structures, calculated by using AIMALL software. The bond length (Na-H) of (Na H) n (n=1-6) clusters, have been found to be in the range (1.790 to 2.120) ˚A for linear structures at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. Similarly, we have analyzed the cubic and cubic like structure of sodium hydride tetramer and sodium hydride hexamer but no cubic like structures are formed in sodium hydride pentamer.
Keywords: Sodium hydride clusters, Interaction energy, Frequency, BSSE, DFT
- INTRODUCTION
Computational physics is the method of studying numerical algorithms and implementing them to solve problems in physics for which a quantitative theory already exists. Historically, it was the first application of modern computers in science and it is now a subset of computational science. It is also considered as the intermediate part between theoretical and experimental physics [1]. Computational physics also uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids. It is fairly inexpensive, speedy and environmentally safe compared to the experimental work [2]. Moreover, computation become so reliable in some respects that more and more, scientists in general are employing it before starting on an experimental work and the day may come when to obtain a grant for some kinds of experimental work, we will have to execute to what extent we have computationally explored the practicability of the proposal [3].There are many different types of clusters, such as metallic clusters, molecular clusters , semiconductor clusters, organic clusters, van der Waals clusters and ionic clusters, which all have their own features and properties [4]. Solid cluster is a group of atoms or molecules. When there is transfer of electrons form one atom to other, each atom needs stable configuration similar to the close nascent gas atoms. Such kind of bonding is known as ionic bond. Simply, cation means atoms that loses one or more electrons and anion means atoms that gains one or more electrons [5]. Some examples of ionic crystals are Na H, LiH, NaCl, NaBr, KF, K Cl, Al2O3, etc. Compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic [6]. Compounds of non-metals with non- metals will be covalent. The common example of ionic bonding is the sodium hydride bonding which add the subject of interest in the present work. As we know, sodium and hydrogen be Ing the element of the same s-block, so it is more interesting. Sodium is metallic element heavier than lithium element. It is more reactive than Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium and Francium. Sodium has potential to form multicentered bonds (i. e, “hypervalent” clusters with more “bonds” than available valence electrons) has been a focus of attention for many years [7]. Sodium hydride is after Ne H. Sodium hydrides are important as models for simple electron-deficient ionic metal compounds [8]. The first-principles calculations have been carried out to study the stability, electronic structures and properties such as ground state energy, dipole moment, interaction energy, electronic distribution etc. of a wide range of solid systems using the Gaussian 98 suit of programs in the last few years and recently using the Gaussian 03W suit of programs [9] in the Central Department of Physics in collaboration with the State University of New York at Albany. With the availability of the Gaussian 98 and the Gaussian 03W suit of programs, the ab-initio calculations have been performed to study the equilibrium configurations for magnesium monohydride and its dimer, beryllium hydride and beryllium monohydride clusters, alkali metal hydrides, lithium hydride and lithium dihydride, sodium hydride etc [10]. also have been carried out in the Central Department of Physics, Kantipur, Nepal. In the present work, we focus mainly on equilibrium configuration, interaction energy, zero-point energy and harmonic vibrational frequency of (Na H) n clusters. In the present study, we target to determine stable structure of sodium hydride clusters [11]. The inconsistency of basis set was eliminated by basis set superposition error (BSSE). We have also determined the nature of bonding in sodium hydride clusters. The QTAIM calculation was done using choice of basis sets and assist of wave function using AIMALL software [12].
- MATERIALS AND METHODS
The clusters or solids are systems composed by mutually interacting electrons and nuclei and the dynamics of these particles. In general, it cannot be considered separately. Many properties of the interacting system can be obtained by determining the eigenfunction which is the fundamental problem in many bodies system. The total Hamiltonian [13] of a system of N mutually interacting electrons and M nuclei. Born-Oppenheimer Approximation is the first of the several approximations used to simplify the solution of the Schrodinger equation. It simplifies the general molecular problem by separating nuclear and electronic
- RESULT & DISCUSSION
Interaction energy (EI) [27] of all (Na H) n, (n=1-6) clusters are calculated by using formula below,
EI = E [(Na H) n] – E [(Na H) n−1 – E [Na H]
Where, E [(Na H) n], E [(Na H) n−1, E [Na H] are optimized energies of present cluster, succeed cluster and Na H cluster respectively. Having more negative interaction energy of the structure to be more stable as compared to other structures.
Similarly, we have calculated corrected zero-point energy EZP by using following formula.
EZP = E’cluster− E’compone Σnts
EZP = E [(Na H) n] – n E [Na H]
Where, E [(Na H) n] represent the zero-point vibrational energy of present cluster and E [Na H] is the zero point vibrational energy of (Na H) cluster.
We have used the below formula to calculate the interaction energy with corrected zero-point energy EI+ZP of (Na H) n clusters is,
EI+ZP = EI + EZP
ΔE = EI+ZP + Eb
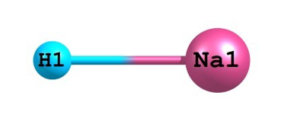
Figure 01: Optimized structure of sodium hydride monomer at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using basis set 6-311++G**.
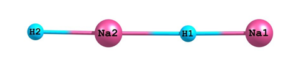
Figure 02: Optimized linear structure of sodium hydride dimer at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using basis set 6-311++G**.
Table 01: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP, basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of linear structure of sodium hydride dimer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using basis sets 6- 31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00164 | -203798 | 1.259 | -22.590 | -21.331 | -21.329 |
| B3LYP | 0.00093 | -204398 | 1.405 | -20.080 | -18.675 | -18.673 | |
| MP2 | 0.00200 | -203814 | 1.379 | -21.960 | -20.581 | -20.578 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00169 | -203799 | 1.335 | -21.335 | -20.000 | -19.998 |
| B3LYP | 0.00108 | -204399 | 1.288 | -19.452 | -18.164 | -18.162 | |
| MP2 | 0.00254 | -203818 | 1.226 | -21.962 | -20.736 | -20.733 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00072 | -203805 | 1.507 | -21.962 | -20.455 | -20.454 |
| B3LYP | 0.00069 | -203937 | 1.347 | -25.727 | -24.380 | -24.379 | |
| MP2 | 0.00109 | -203821 | 1.421 | -20.700 | -19.279 | -19.277 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00064 | -203807 | 1.443 | -22.590 | -21.147 | -21.146 |
| B3LYP | 0.00088 | -204409 | 1.574 | -20.706 | -19.132 | -19.131 | |
| MP2 | 0.00143 | -203835 | 1.265 | -21.335 | -20.070 | -20.068 |
Table 02: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cyclic structure of sodium hydride dimer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has tabulated below
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00146 | -203813 | 2.381 | -37.650 | -35.269 | -35.267 |
| B3LYP | 0.001093 | -204413 | 2.359 | -43.512 | -41.153 | -41.510 | |
| MP2 | 0.00325 | -203828 | 2.339 | -36.395 | -34.056 | -34.052 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00141 | -203816 | 2.345 | -38.905 | -36.560 | -36.558 |
| B3LYP | 0.00111 | -204414 | 2.341 | -35.140 | -32.799 | -32.797 | |
| MP2 | 0.00475 | -203835 | 2.154 | -38.905 | -36.751 | -36.746 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00047 | -203820 | 2.327 | -37.022 | -34.695 | -34.694 |
| B3LYP | 0.00699 | -204422 | 2.266 | -43.925 | -41.659 | -41.652 | |
| MP2 | 0.00262 | -203830 | 2.264 | -28.865 | -26.601 | -26.598 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00034 | -203823 | 2.335 | -38.905 | -36.570 | -36.569 |
| B3LYP | 0.00088 | -204424 | 2.339 | -35.140 | -32 | -32.800 | |
| MP2 | 0.00060 | -203843 | 2.404 | -29.492 | -27.088 | -27.084 |
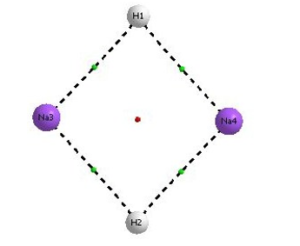
Figure 03: Cyclic structure of sodium hydride dimer with bond critical point at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using basis set 6-311++G**.

Figure 04: Optimized linear structure of sodium hydride trimer at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using basis set 6-311++G**.
Table 03: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of linear structure of sodium hydride trimer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00152 | -305715 | 3.121 | -29.492 | -26.371 | -26.369 |
| B3LYP | 0.00087 | -306613 | 2.960 | -26.355 | -23.395 | -23.394 | |
| MP2 | 0.00208 | -305737 | 2.960 | -27.610 | -24.650 | -24.647 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00148 | -305717 | 2.833 | -49.572 | -46.739 | -46.737 |
| B3LYP | 0.00094 | -306614 | 2.693 | -25.727 | -23.034 | -23.031 | |
| MP2 | 0.00257 | -305744 | 2.452 | -27.484 | -25.032 | -25.029 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00064 | -305726 | 3.150 | -28.865 | -25.715 | -25.714 |
| B3LYP | 0.00064 | -306627 | 2.866 | -38.579 | -35.724 | -35.723 | |
| MP2 | 0.00117 | -305749 | 2.880 | -27.610 | -24.730 | -24.728 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00056 | -305727 | 3.119 | -28.237 | -25.118 | -25.117 |
| B3LYP | 0.00087 | -306629 | 3.437 | -25.727 | -22.290 | -22.289 | |
| MP2 | 0.00163 | -305769 | 2.427 | -28.237 | -25.710 | -25.708 |
Table 04: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cyclic structure of sodium hydride trimer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00267 | -305744 | 4.505 | -43.297 | -38.792 | -38.789 |
| B3LYP | 0.00179 | -306642 | 4.444 | -40.787 | -36.343 | -36.341 | |
| MP2 | 0.00471 | -305767 | 4.465 | -36.395 | -31.930 | -31.925 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00259 | -305747 | 4.401 | -42.670 | -38.269 | -38.266 |
| B3LYP | 0.00176 | -306644 | 4.348 | -40.160 | -35.812 | -35.810 | |
| MP2 | 0.00627 | -305775 | 4.474 | -42.670 | -38.196 | -38.189 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00092 | -305754 | 4.475 | -42.670 | -38.195 | -38.194 |
| B3LYP | 0.00104 | -306656 | 4.347 | -33.132 | -28.785 | -28.783 | |
| MP2 | 0.00322 | -305778 | 4.443 | -43.297 | -38.854 | -38.850 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00062 | -305758 | 4.397 | -42.042 | -37.645 | -37.644 |
| B3LYP | 0.00082 | -306659 | 4.380 | -40.160 | -35.780 | -35.779 | |
| MP2 | 0.00396 | -305801 | 4.487 | -52.082 | -47.595 | -47.591 |
Table 05: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of linear structure of sodium hydride tetramer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6- 31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has tabulated below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00307 | -407634 | 4.693 | -30.747 | -26.054 | -26.050 |
| B3LYP | 0.00175 | -408831 | 4.472 | -28.237 | -23.765 | -23.763 | |
| MP2 | 0.00417 | -407664 | 4.423 | -30.120 | -25.697 | -25.692 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00317 | -407636 | 4.426 | -32.002 | -27.576 | -27.572 |
| B3LYP | 0.00199 | -408832 | 4.101 | -28.237 | -24.136 | -24.134 | |
| MP2 | 0.00522 | -407672 | 3.728 | -30.120 | -26.392 | -26.386 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00125 | -407647 | 4.767 | -30.120 | -25.353 | -25.351 |
| B3LYP | 0.00135 | -408832 | 4.468 | -33.320 | -28.852 | -28.850 | |
| MP2 | 0.00225 | -407672 | 4.395 | -28.865 | -24.470 | -24.847 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00105 | -407650 | 4.811 | -32.002 | -27.191 | -27.189 |
| B3LYP | 0.00148 | -408851 | 5.334 | -27.610 | -22.276 | -22.274 | |
| MP2 | 0.00374 | -407744 | 6.032 | -68.397 | -62.365 | -62.361 |
Table 06: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cyclic structure of sodium hydride tetramer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6- 31G*, 6-311+G, 6-311++G** basis sets has tabulated below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00264 | -407670 | 6.128 | -37.650 | -31.522 | -31.519 |
| B3LYP | 0.00175 | -408866 | 6.132 | -35.140 | -29.008 | -29.006 | |
| MP2 | 0.00452 | -407699 | 6.061 | -33.885 | -27.824 | -27.819 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00271 | -407672 | 5.939 | -39.532 | -33.593 | -33.590 |
| B3LYP | 0.00184 | -408868 | 5.952 | -34.512 | -28.560 | -28.558 | |
| MP2 | 0.00621 | -407710 | 6.012 | -37.022 | -31.010 | -31.003 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00087 | -407683 | 6.126 | -37.022 | -30.896 | -30.895 |
| B3LYP | 0.00092 | -408885 | 5.995 | -32.630 | -26.635 | -26.634 | |
| MP2 | 0.00290 | -439089 | 6.010 | -56.475 | -50.465 | -50.462 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00057 | -407687 | 5.946 | -37.022 | -31.076 | -31.075 |
| B3LYP | 0.00082 | -408888 | 6.027 | -33.885 | -27.858 | -27.857 | |
| MP2 | 0.00374 | -407744 | 6.033 | -36.395 | -30.362 | -30.358 |
Table 07: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP, basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cubic structure of sodium hydride tetramer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6- 31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has tabulated below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00238 | -407667 | 7.199 | -34.512 | -27.313 | -27.310 |
| B3LYP | 0.00213 | -408865 | 7.171 | -33.885 | -26.714 | -26.711 | |
| MP2 | 0.00635 | -407671 | 7.275 | -39.595 | -22.320 | -22.313 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00220 | -408868 | 6.972 | -35.767 | -28.795 | -28.792 |
| B3LYP | 0.00196 | -408868 | 7.046 | -34.512 | -27.466 | -27.464 | |
| MP2 | 0.00803 | -407712 | 7.390 | -38.905 | -31.515 | -31.506 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00151 | -407680 | 7.989 | -34.512 | -27.523 | -27.521 |
| B3LYP | 0.00195 | -408884 | 6.902 | -32.504 | -25.602 | -25.600 | |
| MP2 | 0.00579 | -407858 | 6.121 | -35.767 | -28.646 | -28.600 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00095 | -407687 | 6.984 | -37.022 | -30.038 | -30.037 |
| B3LYP | 0.00197 | -408889 | 7.011 | -28.129 | -21.118 | -21.110 | |
| MP2 | 0.00578 | -407748 | 7.325 | -40.160 | -32.810 | -32.804 |
Table 08: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of linear structure of sodium hydride pentamer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00144 | -509554 | 6.166 | -32.002 | -25.836 | -25.834 |
| B3LYP | 0.00084 | -511049 | 5.926 | -29.492 | -23.566 | -23.565 | |
| MP2 | 0.00210 | -509591 | 5.846 | -31.375 | -25.529 | -25.526 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00141 | -509556 | 5.663 | -31.375 | -25.712 | -25.710 |
| B3LYP | 0.00090 | -511051 | 5.518 | -29.492 | -23.974 | -23.973 | |
| MP2 | 0.00266 | -509601 | 5.051 | -31.375 | -26.324 | -26.321 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00065 | -509570 | 6.273 | -31.375 | -25.102 | -25.101 |
| B3LYP | 0.00070 | -511072 | 5.533 | -32.002 | -26.469 | -26.468 | |
| MP2 | 0.00124 | -509610 | 7.743 | -30.747 | -25.004 | -25.002 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00052 | -509573 | 6.396 | -31.375 | -24.979 | -24.978 |
| B3LYP | 0.00082 | -511075 | 7.220 | -28.865 | -21.645 | -21,644 | |
| MP2 | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO |
Table 09: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cyclic structure of sodium hydride pentamer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 level of theory using basis sets 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(Kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00296 | -509593 | 7.621 | -35.767 | -28.146 | -28.143 |
| B3LYP | 0.00189 | -511089 | 7.570 | -33.885 | -26.315 | -26.133 | |
| MP2 | 0.00482 | -509630 | 7.544 | -35.140 | -27.596 | -27.591 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00301 | -509596 | 7.348 | -35.140 | -27.792 | -27.788 |
| B3LYP | 0.00187 | -511089 | 7.288 | -31.375 | -24.087 | -24.085 | |
| MP2 | 0.00644 | -509642 | 7.452 | -34.512 | -27.060 | -27.053 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00103 | -509610 | 7.686 | -35.140 | -27.454 | -27.452 |
| B3LYP | 0.00092 | -511112 | 7.434 | -34.073 | -26.396 | -26.368 | |
| MP2 | 0.00295 | -509649 | 7.463 | -34.512 | -27.049 | -27.046 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00061 | -509613 | 7.361 | -34.512 | -27.151 | -27.150 |
| B3LYP | 0.00077 | -511109 | 7.381 | -31.375 | -23.994 | -23.993 | |
| MP2 | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO |
Table 10: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of linear structure of sodium hydride hexamer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using basis sets 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** has shown below.
UTO denote the unable to optimize.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00143 | -611474 | 7.667 | -32.002 | -24.335 | -24.333 |
| B3LYP | 0.00084 | -613268 | 7.439 | -30.120 | -22.681 | -22.680 | |
| MP2 | 0.00209 | -611518 | 7.275 | -31.375 | -24.100 | -24.087 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00140 | -611476 | 7.051 | -32.002 | -24.951 | -24.949 |
| B3LYP | 0.00089 | -613270 | 6.876 | -28.865 | -21.989 | -21.988 | |
| MP2 | 0.00265 | -611530 | 6.192 | -28.865 | -22.673 | -22.670 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00065 | -611494 | 7.797 | -32.002 | -24.205 | -24.202 |
| B3LYP | 0.00070 | -613296 | 7.374 | -32.065 | -24.691 | -24.690 | |
| MP2 | 0.00125 | -611540 | 7.119 | -30.120 | -23.001 | -22.999 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00052 | -611497 | 7.998 | -31.375 | -23.377 | -23.376 |
| B3LYP | 0.00081 | -613299 | 9.027 | -29.492 | -20.465 | -20.464 | |
| MP2 | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO |
![]()
Figure 05: Linear structure of sodium hydride hexamer with bond critical point at DFT(B3LYP) level of approximation using basis set 6-311++G**.
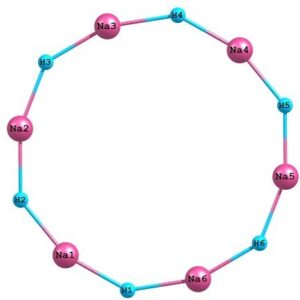
Figure 06: Optimized cyclic structure of sodium hydride hexamer at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using basis set 6-311++G**.
Table 11: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero point energy EZP , basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero point energy EI+ZP , corrected interaction energy ΔE of cyclic structure of sodium hydride hexamer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using basis sets 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** has shown below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00294 | -611516 | 9.068 | -34.512 | -25.444 | -25.441 |
| B3LYP | 0.00193 | -613310 | 9.049 | -32.002 | -22.953 | -22.951 | |
| MP2 | 0.00208 | -611518 | 7.235 | -35.361 | -28.126 | -28.123 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00301 | -611519 | 8.695 | -34.512 | -25.817 | -28.123 |
| B3LYP | 0.00194 | -613313 | 8.663 | -28.785 | -20.122 | -20.120 | |
| MP2 | 0.00640 | -611575 | 8.822 | -34.512 | -25.690 | -25.683 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00105 | -611536 | 9.202 | -34.512 | -25.310 | -25.308 |
| B3LYP | 0.00100 | -613338 | 8.191 | -32.316 | -23.397 | -23.396 | |
| MP2 | 0.00281 | -611582 | 8.841 | -32.630 | -23.789 | -23.786 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00062 | -611540 | 8.714 | -33.885 | -25.171 | -25.170 |
| B3LYP | 0.00084 | -613341 | 8.754 | -31.375 | -22.621 | -22.620 | |
| MP2 | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO |
Table 12: Interaction energy EI, ground state energy Emin, corrected zero-point energy EZP, basis set superposition error Eb, interaction energy with corrected zero-point energy EI+ZP, corrected interaction energy ΔE of cubic like structure of sodium hydride hexamer at HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels of theory using basis sets 6- 31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** has tabulated below.
| Basis Sets | Level of
Theory |
Eb
(kcal mol−1 ) |
Emin
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI
(kcal mol−1 ) |
EI+ZP
(kcal mol−1 ) |
ΔE
(kcal mol−1 ) |
|
6-31+G |
HF | 0.00308 | -611522 | 11.206 | -40.787 | -29.581 | -29.577 |
| B3LYP | 0.00341 | -613319 | 11.155 | -40.160 | -29.005 | -29.001 | |
| MP2 | 0.00774 | -611570 | 11.472 | -43.925 | -32.453 | -32.445 | |
|
6-31G∗ |
HF | 0.00284 | -611528 | 10.791 | -43.297 | -32.506 | -32.503 |
| B3LYP | 0.00314 | -613322 | 10.828 | -43.297 | -32.469 | -32.465 | |
| MP2 | 0.00937 | -611589 | 11.382 | -48.945 | -37.563 | -37.553 | |
|
6-311+G |
HF | 0.00191 | -611542 | 10.937 | -40.787 | -29.850 | -29.848 |
| B3LYP | 0.00243 | -613347 | 10.819 | -33.194 | -22.375 | -22.372 | |
| MP2 | 0.00657 | -611593 | 11.088 | -43.297 | -32.209 | -32.202 | |
|
6-311++G∗∗ |
HF | 0.00138 | -611550 | 10.862 | -43.925 | -33.063 | -33.061 |
| B3LYP | 0.00227 | -613352 | 10.980 | -42.670 | -31.690 | -31.687 | |
| MP2 | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO | UTO |
- CONCLUSION
All the calculations obtained from the entire work are based on first principles method. We have used three different theories: HF, DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels. We have obtained better results in DFT(B3LYP) and MP2 levels than HF level. We have performed the first principles calculation to study the ground state energy, corrected zero-point energy, interaction energy, interaction energy with corrected zero-point energy, corrected interaction energy, BSSE, maximum and minimum frequency of (Na H) n clusters (n=1-6) and we have studied electron density of bond critical point (ρ bcp) and Laplacians(∇2ρ) of (Na H) n clusters (n=1-6) using AIM calculations. We have selected 6-31+G, 6-31G*, 6-311+G and 6-311++G** basis sets and performed whole work using G03W and AIMALL software. Linear and cyclic structures were found in all (Na H) n clusters (n=1-6) but cubic structures were found only in sodium hydride tetramer and sodium hydride hexamer clusters. In sodium hydride dimer, we have calculated ground state energy, zero-point vibrational energy and corrected interaction energy whose values are -204409 kcal mol−1, 4.924 kcal mol−1 and -19.131 kcal mol−1 respectively for linear structure and -204424 kcal mol−1, 5.689 kcal mol−1 and -32.800 kcal mol−1 respectively for cyclic structure at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. In sodium hydride trimer, we have determined the ground state energy, zero-point vibrational energy and corrected interaction energy with values are -306629 kcal mol−1, 8.462 kcal mol−1 and -22.289 kcal mol−1 respectively for linear structure and -306659 kcal mol−1,9.405 kcal mol−1 and -35.779 kcal mol−1 respectively for cyclic structure at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. In sodium hydride tetramer, the calculated values of the ground state energy, zero point vibrational energy and corrected interaction energy are -408851 kcal mol−1, 12.034 kcal mol−1 and -22.274 kcal mol−1 respectively for linear structure, -408888 kcal mol−1, 12.727 kcal mol−1 and -27.857 kcal mol−1 respectively for cyclic structure and -408889 kcal mol−1, 13.711 kcal mol−1 and -28.127 kcal mol−1 respectively for cube structure at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. Similarly, two structures of sodium hydride pentamer have been studied. The calculated ground state energy, zero-point vibrational energy and corrected interaction energy values are -509593 kcal mol−1, 15.595 kcal mol−1 and -21.644 kcal mol−1 respectively for linear structure and -511109 kcal mol−1, 15.756 kcal mol−1 and -23.993 kcal mol−1 for cyclic structure at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6-311++G** basis set. In addition, three structures of sodium hydride hexamer have been studied. we have determined the ground state energy, zero point vibrational energy and corrected interaction energy values are -613299 kcal mol−1, 19.077 kcal mol−1 and -20.464 kcal mol−1 respectively for linear structure, -613341 kcal mol−1, 18.804 kcal mol−1 and -22.620 kcal mol−1 respectively for cyclic structure and -613352 kcal mol−1, 21.030 kcal mol−1 and -31.687 kcal mol−1 respectively for cube like structure at DFT(B3LYP) level of theory using 6- 311++G** basis set. We have also calculated the maximum and minimum frequency of all kind of clusters (Na H) n, (n=1-6). In the entire work we have also calculated the electron density at bond critical point (ρ bcp) and Laplacians (∇2ρ) of all structures of sodium hydride clusters (Na H) n, (n=1-6). Finally, we have studied, calculated and discussed about the all structures of sodium hydride clusters in the entire present work.
References
- Lewars, Introduction to Theory and Application of Molecular and Quantum Mech- nics, New York, (2004).
- K. Puri and V. K. Babbar, Solid State Physics, S. Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi, Third Edition, (2008).
- J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheese- man, J. A. Montgomery, Jr., T. Vreven, K. N. Kudin, J. C. Burant, J. M. Millam, S.
- Iyengar, J. Tomasi, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, M. Cossi, G. Scalmani, N. Rega, G. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa,
- Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, M. Klene, X. Li, J. E. Knox,
- P. Hratchian, J. B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R. E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A. J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J. W. Ochterski, P. Y. Ayala, K. Morokuma, G. A. Voth, P. Salvador, J. J. Dannenberg, V. G. Zakrzewski,
- Dapprich, A. D. Daniels, M. C. Strain, O. Farkas, D. K. Malick, A. D. Rabuck,
- Raghavachari, J. B. Foresman, J. V. Ortiz, Q. Cui, A. G. Baboul, S. Clifford, J. Cioslowski, B. B. Stefanov, G. Liu, A. Liashenko, P. Piskorz, I. Komaromi, R. L. Martin, D. J. Fox, T. Keith, M. A. Al-Laham, C. Y. Peng, A. Nanayakkara, M. Chal- lacombe, P. M. W. Gill, B. Johnson, W. Chen, M. W. Wong, C. Gonzalez, and J. A. Pople, Gaussian 03, Revision E.01, Wallingford CT, (2004).
- A. Keith, AIMALL (Version 11.12.19) Gristmill Software, Overland Park KS, USA, 2011.
- Parajuli and E. Arunan, Chem. Phys. Lett. 568-569, 63 (2013).
- R. Upadhyaya, Structure and Electronic Properties of (LiH)n Clusters (n=1-7), M.Sc. (Physics) Dissertation, Amrit Campus, Tribhuvan University, Nepal (2013).
- Sapkota, Computational Study of Hydrogen Bonding in CH3CN• • •(HX)n[X=F, Cl, NH2, n=1, 2] Complexes, M.Sc. (Physics) Dissertation, Amrit Campus, Tribhuvan University, Nepal (2015).
- F. Matta and R. J. Boyd, The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, (2007).
Publication History
Submitted: April 27, 2024
Accepted: May 22, 2024
Published: February 28, 2025
Identification
D-0347
DOI
https://doi.org/10.71017/djnsi.4.2.d-0347
Citation
Kamal Giri (2025). First Principles Study of Stability of Sodium Hydride (Nah)N Clusters, (N=1-6). Dinkum Journal of Natural & Scientific Innovations, 4(02):92-103.
Copyright
© 2025 The Author(s).


